Basal Cell Carcinoma Facts
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinomas originate in keratinocytes (cells that produces keratin) located in the basal layer of the epidermis — your skin's outermost layer. Although these tumors have low metastatic potential, they can invade locally and be destructive to your skin and surrounding structures, including bone.
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most critical factor in the development of basal cell carcinoma. This may occur from sun exposure or tanning bed use or be exacerbated by health conditions that increase photosensitivity, etc. People with fair skin and a tendency to sunburn are more likely to develop basal cells than people with darker skin. Other risk factors for the development of basal cell carcinoma include immunosuppression and certain inherited genetic disorders.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma?
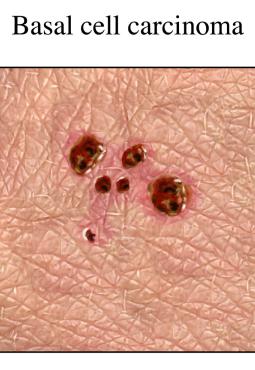
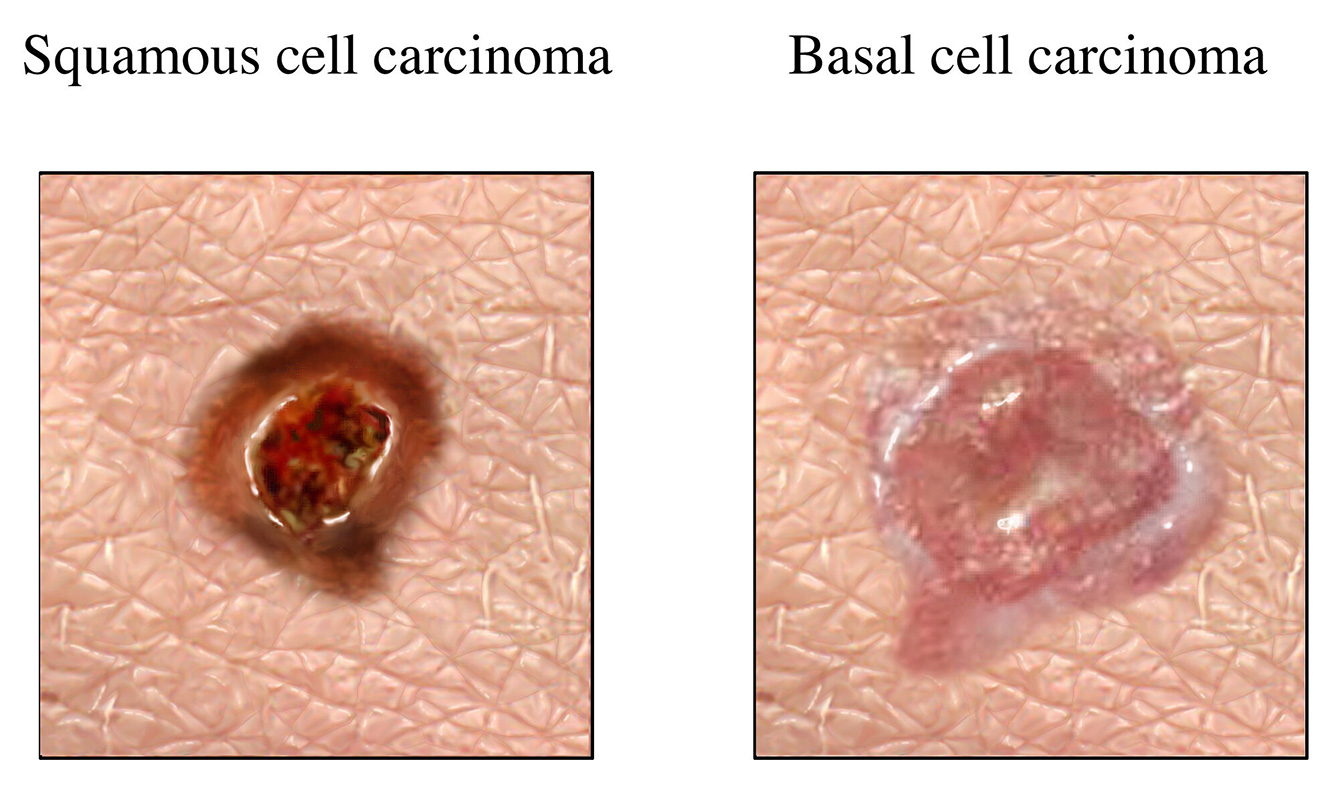
Basal cell carcinoma appears as sores that won't heal or as pink, shiny bumps that grow and have a tendency to erode or bleed.
Other symptoms may include:
- Pinkish patches with shiny, pearly-white raised edges
- Nonhealing, bleeding or crusting open sores
- Red or bleeding scaly patches
- Wart-like growths with crusted surfaces
- Hard, waxy skin lumps with visible blood cells
- A newly itchy, tender or painful sore
If you notice any of these skin changes, contact your doctor.
The stages of skin cancer are defined by the structures that are involved:
- T-stage describes how deeply the tumor has invaded the skin and nearby tissues.
- N-stage is the tumor’s involvement in nearby lymph nodes.
- M-stage describes whether or not the cancer cells have spread to distant organs.
Basal cell carcinoma is less likely than other skin cancers to spread to your lymph nodes and distant organs.
The main risk factor for developing basal cell carcinoma is exposure to ultraviolet radiation from:
- Natural sunlight
- Tanning beds
- Sun lamps
Other factors that may contribute to developing basal cell carcinoma include:
- Having a history of severe, blistering sunburns
- Being a blond or redhead
- Having fair skin that easily freckles or sunburns
- Having light-colored, blue or green eyes
- Family history of skin cancer
- Having a weakened immune system
- Previously being diagnosed with skin cancer
- Previously having radiation therapy
- Having actinic keratosis
- Having Gorlin syndrome
- Having a rare inherited condition called xeroderma pigmentosum

Ultraviolet damage is cumulative, meaning it begins building up in your childhood, so prevention should start at a young age. The best ways to lower your risk for skin cancer include shielding the skin as much as possible from UV radiation:
- Use sunscreen and reapply at least every two hours
- Wear protective clothing, including fabrics not easily penetrated by UV light
- Wear other protective items such as hats and sunglasses
- Stay in the shade during peak hours when the sun’s UV rays are most intense (from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
- Avoid tanning salons