Ovarian Cancer Facts
What is Ovarian Cancer?
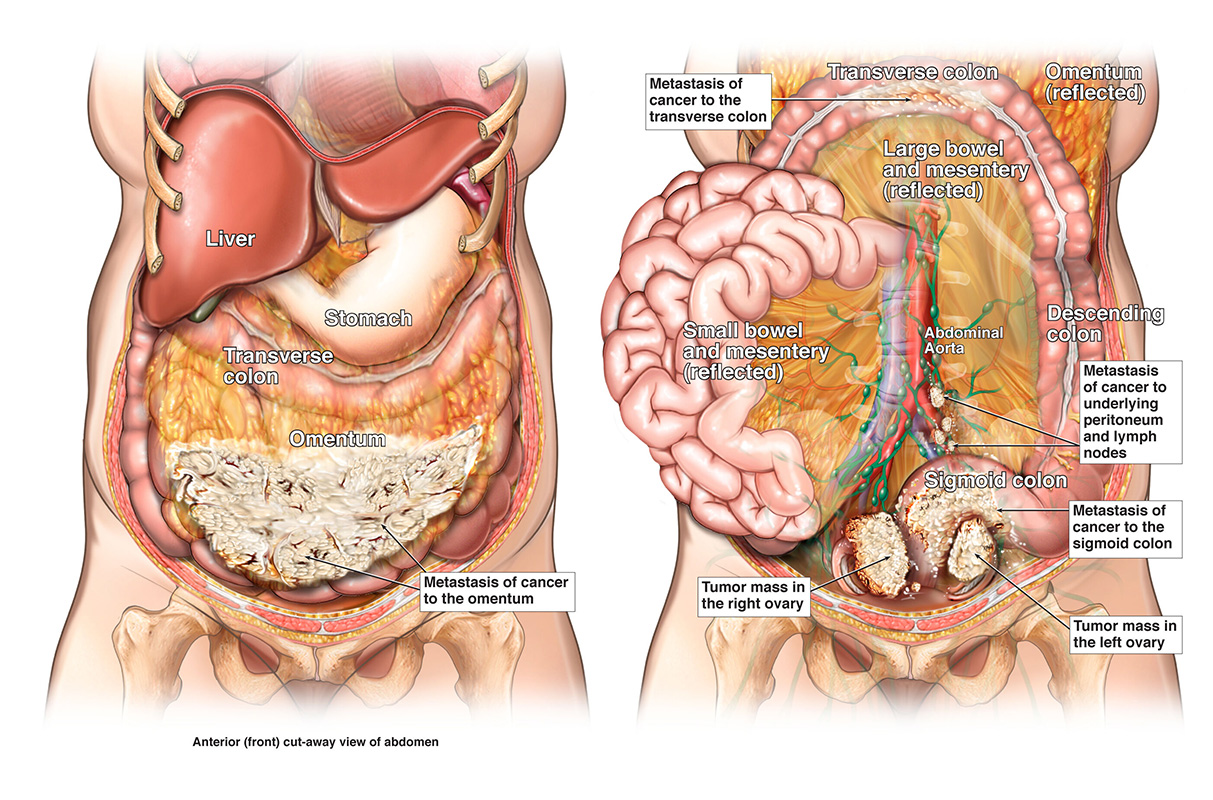
Ovarian cancer is a disease in which cells of the ovaries divide uncontrollably, invading nearby tissues and possibly spreading to other areas of the body.
There are several types of cancerous ovarian tumors, depending on the type of cell that is affected. The major ones include:
- Epithelial tumors: Approximately 90 percent of ovarian tumors are of this type, involving cells lining ovary’s outer surface.
- Germ cell tumors: This type start from cells that produces the ova (eggs).
- Stromal tumors: This cancer comes from the cells that produce the female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
What Risk Factors are Linked to Ovarian Cancer?
Factors that can elevate risk ovarian cancer risk include:
- Age: Ovarian cancer risk increases with age, and ovarian cancers develop after menopause.
- Personal or family history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer or colorectal cancer
- Hormone therapy, particularly estrogen-only therapy for more than five years
- Inherited cancer syndromes, including BRCA gene mutations, hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (also known as HNPCC or Lynch syndrome), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and MUTYH-associated polyposis
- Reproductive history: Women who have never given birth or gave birth after the age of 35 have a greater ovarian cancer risk.
- Endometriosis, a condition in which uterine lining grows outside of the uterus
Research has also shown that a low-fat diet and use of oral or injectable contraceptives may lower ovarian cancer risk. Some studies also show that aspirin and acetaminophen use may lower ovarian cancer risk. However, the results have not been consistent and women should not take these drugs solely for lowering ovarian cancer risk.
Ovarian cancer risk may also be reduced by prophylactic surgeries, such undergoing tubal ligation (severing, blocking or tying off the fallopian tubes), hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) and/or oophorectomy (surgical removal of the ovaries). These methods are typically reserved for women with a greatly elevated risk of developing ovarian cancer, such as BRCA mutation carriers.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- Pelvic, abdominal or back pain
- Bloating
- Loss of appetite or feeling full quickly
- Urinary symptoms, such as increased urgency or frequency
- Menstrual changes
- Pain during sex
- Constipation
- Fatigue
Although these symptoms can be caused by other conditions, you should check with your doctor to get a definitive diagnosis.
Sources: National Cancer Institute and American Cancer Society