Skin Cancer Facts
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and, in most cases, it is not life-threatening nor does it spread to other parts of the body. The exception is melanoma, the rarest and most aggressive form of skin cancer.
According to the American Cancer Society, more than 5 million nonmelanoma skin cancers (basal and squamous cell cancers) are expected to be diagnosed in 2024. In 2024, melanoma will be diagnosed in approximately 100,640 people. An estimated 8,290 people will die of melanoma in 2024.
Types of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Most often develops on sun-exposed sites of the skin (face, neck, shoulders) as pink and shiny bumps that grow and have a tendency to erode and/or bleed.
- Typically affects only the skin but can lead to significant disfigurement.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Most often develops in sun-exposed sites of the skin as pink and scaly bumps that grow and have a tendency to erode and/or bleed.
- Early detection is critical since these skin cancers can spread to other parts of the body and lead to death.
Melanoma
- An estimated 9,320 people will die of melanoma in 2018.
- The majority of melanoma is caused by the sun, while genetics may also play a role.
- Early detection is critical, as the survival rates worsen with later detection. (The five-year survival rate of Stage 1 melanoma is 98 percent; five-year survival rate is 63 percent for Stage 3 disease and 17 percent for Stage 4 disease.)
Less Common Skin Cancers
- Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive type of skin cancer that develops in sun-exposed skin areas and has a high likelihood of spreading to other body parts.
- Skin lymphoma, also called cutaneous lymphoma, is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that starts in the skin.
- Kaposi sarcoma is a type of cancer that starts in lymph or blood vessel cells and tends to appear in the mouth and as lesions on the skin, but may also develop in the lungs, liver and digestive tract.
- Skin adnexal tumors are tumors that start in hair follicles or skin glands.
- Sarcomas are soft tissue tumors that can begin in deep skin tissue.
Other skin conditions, such as actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma in situ (meaning does not spread to other organs) are precancerous lesions. Early detection is critical to prevent them from becoming skin cancer.
Benign (Noncancerous) Skin Tumors
- Seborrheic keratosis is the most common type of benign skin tumor. Because it may have an asymmetric and evolving shape or irregular edges, it is often mistaken for a cancerous tumor.
- Moles, also called nevi, are common benign (noncancerous) skin growths. Most moles remain benign, but some may evolve into cancers.
- Hemangiomas are raised tumors made up of abnormal collections of blood vessels.
- Lipomas are soft, fatty lumps that develop just under the skin.
- Warts are skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus, also known as HPV.
How Skin Cancer Develops
Skin is an elastic organ — the largest in the body. Its main functions include protecting internal organs, controlling body temperature, shielding the body from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and helping the body make vitamin D. Skin cancer develops when abnormal cells in the skin’s layers grow uncontrollably — most commonly because of too much exposure to UV light from the sun or other sources, like tanning beds and sun lamps.
The most common types of skin cancer — basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas — tend to appear on areas of the body exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, ears and hands.
Melanoma Starts in Melanocytes
Melanoma starts in cells called melanocytes, which are responsible for giving skin its color. This skin pigmentation functions as a shield against harmful ultraviolet (UV) light exposure from the sun, which can lead to mutations in DNA. With enough DNA damage in critical genes the cells of the skin, including melanocytes, begin to grow uncontrollably and spread locally and to distant organs.
Skin Cancer Staging
Skin cancer stages depend on which structures are involved:
- T-stage describes how deeply the tumor has invaded the skin and nearby tissues.
- N-stage is the tumor’s involvement in nearby lymph nodes.
- M-stage describes whether or not the cancer cells have spread to distant organs.
In early skin cancers, the tumors are small, contained within the top layers of skin, and have not spread to distant organs. As the cancer progresses, the tumor grows larger and more deeply into the skin layers, spreading to lymph nodes and blood vessels and, potentially, distant organs.
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are much less likely to spread to lymph nodes and distant organs than melanomas.
What Increases Your Risk of Skin Cancer?
Things that put you at higher risk for getting skin cancer are called risk factors. The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from:
- Sunlight
- Tanning beds
- Sun lamps
Other factors that may contribute to developing skin cancer include:
- Having a history of severe, blistering sunburns
- Having many, or unusual, moles
- Being a blond or redhead, having fair skin that easily freckles or sunburns
- Exposure to large amounts of toxic substances such as paraffin oil, coal tar and arsenic compounds
- Family history of skin cancer
- Previously being diagnosed with skin cancer
- Being older, male
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having a rare inherited condition called xeroderma pigmentosum
People with darker complexions have a much lower risk of most types of skin cancer. When they do develop melanoma, people with darker skin types are much more likely to have rare types of melanoma such as acral lentiginous melanoma, an aggressive type affecting the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and nail bed. Melanoma can also develop in non-sun-exposed areas such as the membranes of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and female genital tract.
Signs of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer signs and symptoms are different from person to person, and for this reason it is one of the more difficult cancers to detect. Most of the time melanoma has no symptoms, although itching may occur and, when it is advanced, so may bleeding.
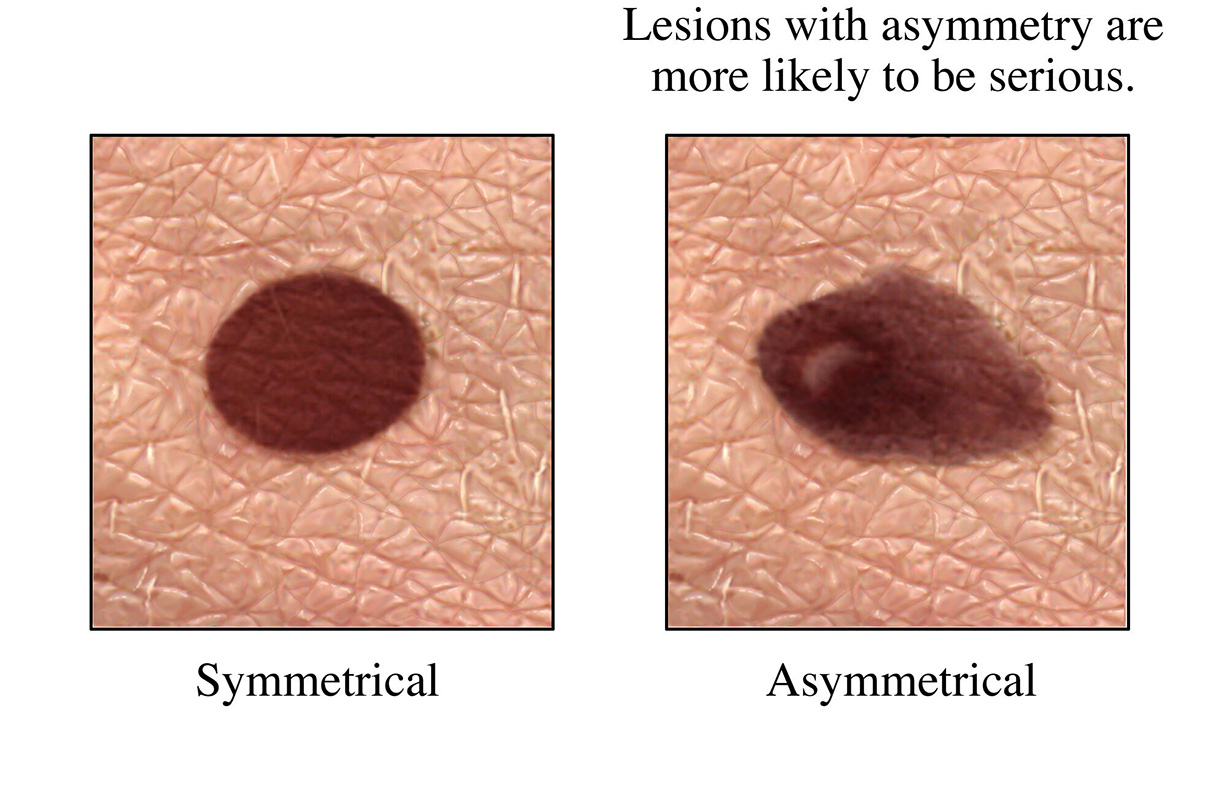
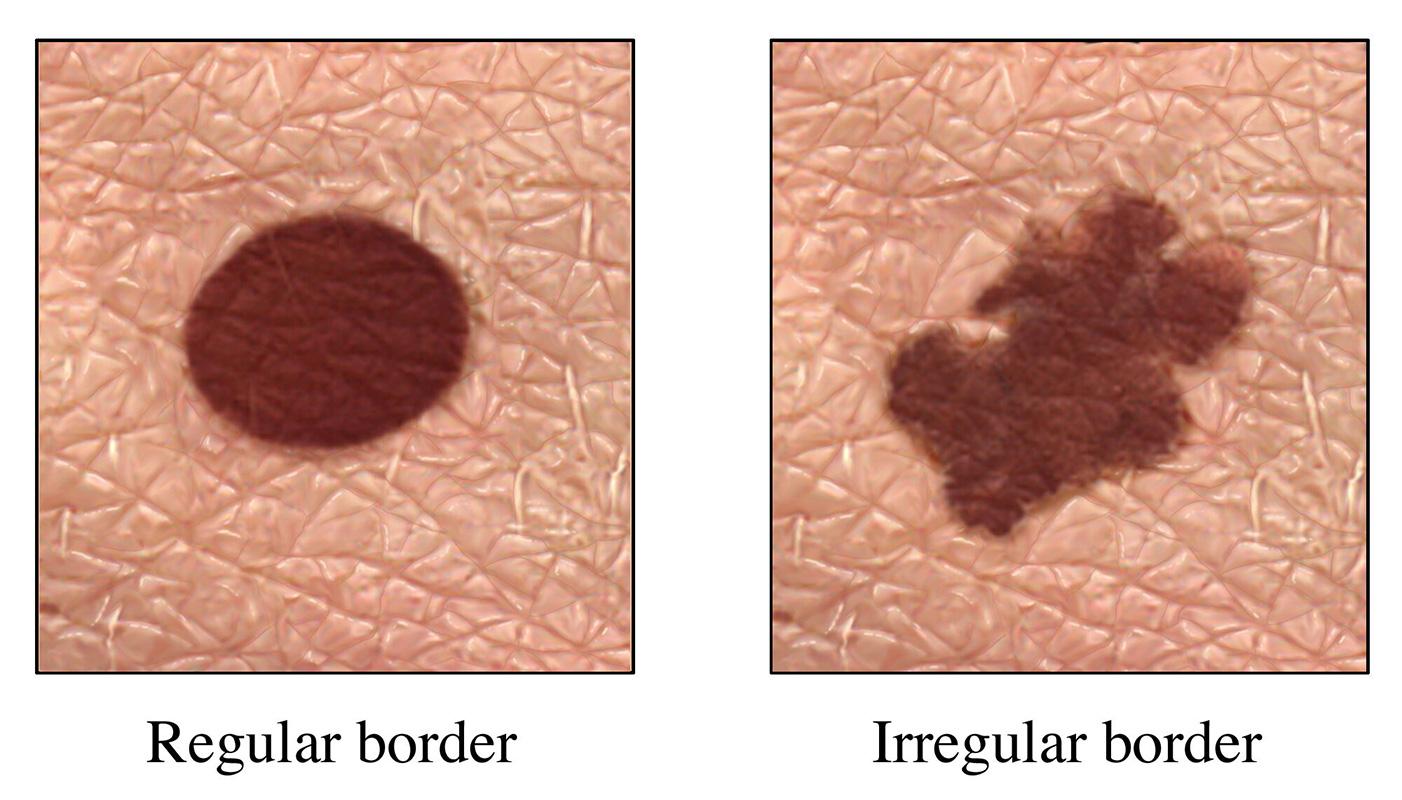
The most important warning sign of skin cancer is a new spot on the skin, especially if that spot changes shape, color or size. Another potential symptom is a spot that looks different from all the others on your skin (known as the “ugly duckling sign”).
Other signs include:
- Red or pink patches with shiny, pearly-white raised edges
- Nonhealing open sores that bleed or develop a crust
- Red scaly patches of skin that may bleed
- Wart-like growths with crusted surfaces
- Hard, waxy skin lumps with visible blood cells
- A newly itchy, tender or painful sore
If you notice any of these skin changes, contact your doctor.
Skin Cancer Prevention
Ultraviolet damage is cumulative, meaning it begins building up in your childhood, so prevention should start at a young age. The best ways to lower your risk for skin cancer include shielding the skin as much as possible from UV radiation:
- Use sunscreen and reapply at least every two hours
- Wear protective clothing, including fabrics not easily penetrated by UV light
- Wear other protective items such as hats and sunglasses
- Stay in the shade during peak hours when the sun’s UV rays are most intense (from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
- Avoid tanning salons
